May is Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome – Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder – Awareness Month. I checked out the Ehlers-Danlos Society and the folowing is a description from their website:
What are these disorders?
The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 heritable connective tissue disorders. The conditions are caused by genetic changes that affect connective tissue. Each type of EDS has its own set of features with distinct diagnostic criteria. Some features are seen across all types of EDS, including joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and tissue fragility.
What is joint hypermobility?
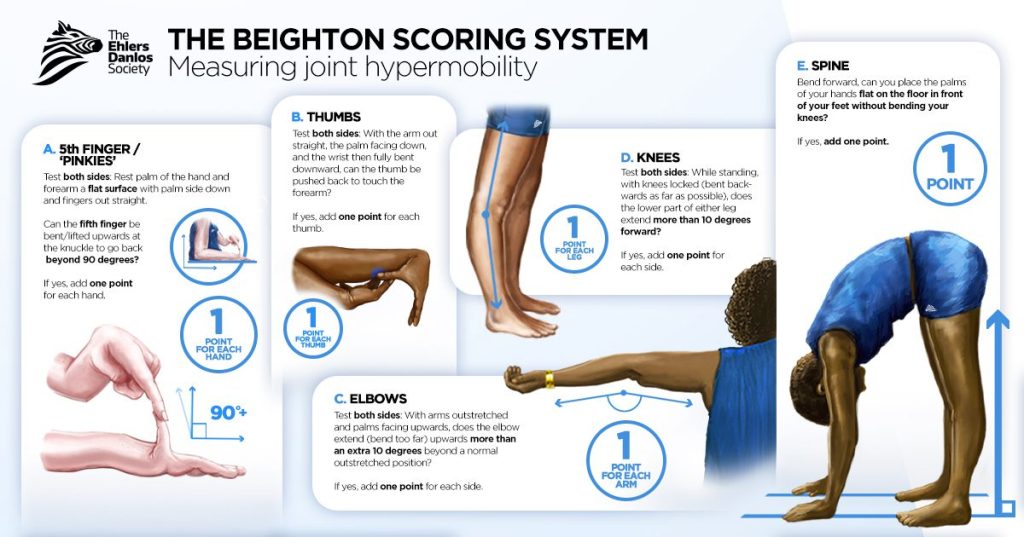
Joint hypermobility means that a person’s joints have a greater range of motion than is expected or usual. Some people have joint hypermobility that does not cause them pain or other issues. However, some people with joint hypermobility also have joint instability. Joint instability occurs when the bones of a joint aren’t held in place securely. This can lead to joint subluxations, dislocations, sprains, and other injuries. Joint instability can cause both acute and chronic pain and interfere with daily life.
Joint hypermobility is observed throughout the body in most types of EDS, but hypermobility may be limited to the hands and feet in some types. Although joint hypermobility is observed across all types of EDS, not everyone with a type of EDS has joint hypermobility. You can read more about joint hypermobility here.
What is skin hyperextensibility?
Skin hyperextensibility means that the skin can be stretched beyond the normal range. Skin extensibility, or skin stretchiness, is measured by pinching and lifting the skin on the volar surface (same side as the palm of the hand) at the middle of the non-dominant forearm. Skin is hyperextensible if it stretches greater than 1.5 cm. Mild skin hyperextensibility may be observed in people with any type of EDS. More severe skin hyperextensibility, greater than 2 cm, is observed in certain types of EDS.
People with a type of EDS may also have other skin characteristics and symptoms, such as unusual skin texture, skin fragility, very thin skin, delayed wound healing, and abnormal scarring. Not everyone with a type of EDS has skin hyperextensibility or unusual skin characteristics.
What is tissue fragility?
Tissue fragility means that the body’s organs and other structures are more vulnerable to damage. Tissue fragility can present as easy bruising and poor wound healing in many types of EDS. Some types of EDS can also cause severe fragility of the skin, blood vessels, abdominal organs, eyes, gums, and bones.
Find out more about EDS and HSD – and how you can help the Society click here

